Cervical Cancer : Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Medically Reviewed by Dr Sravya, MBBS, MS
Introduction
About 70% to 80% of health problems a woman can revel in throughout their lifetime and Cervical cancer is one among them.
Cervical or cervix most cancers are because of a virus called HPV (human papillomavirus), usually in ladies.
Cervical cancer symptoms start with Pelvic pain with watery, bloody heavy vaginal abnormal discharge.
The cervix is part of the decreased uterus connected to the vaginaThe cervix region is mainly get affected by cervical cancer.
When cervix cells multiply abnormally and develop into tumors, cervical cancer occurs.
The HPV virus or other factors could harm the DNA of the cells. Along with the cervical cancer symptoms, the abnormal cells have the potential to develop into cancer over time and spread to other bodily regions(head, neck, etc). Cervical cancers can be effortlessly treated at an early level.
Stages of cervical cancer:
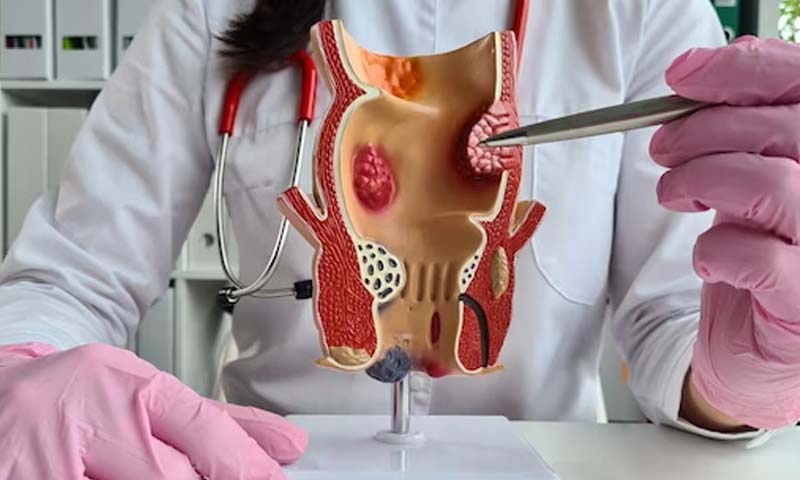
- Stage 0: When the cervix’s inner lining contains abnormal cells.
- Stage 1: Refers to cancer that is limited to the cervix.
- Stage 2: Refers to cancer that has spread beyond the cervix but hasn’t yet reached the pelvic wall.
- Stage 3: In this stage, the cancer has spread to the vagina and possibly the pelvic wall.
- Stage 4: When the cancer has gone to the bladder, rectum, or other body areas through the vaginal.
Cervical cancer types:
Squamous cell cancer or Squamous cell carcinoma
( develops in the thin cells that present on the surface of the cervix, it can be treated with surgery or chemotherapy at the initial stage)
Adenocarcinoma (this type of cervical cancer develops in the cervical canal of epithelial cells. Glandular cells are responsible for lubricating the vaginal area to prevent the infection)
Signs and symptoms of cervical cancer:
Signs and symptoms of cervical cancer may additionally include-
- abnormal vaginal bleeding
- pain during sex
- pelvic pain
- abnormal vaginal discharge.
But suppose you experience any of those signs. In that case, you must talk with your doctor because other health troubles can also arise.

Tests to detect cervical cancer:
Biopsy
(In this a little piece of cervical tissue is taken, and any abnormal cells are checked)
A pap smear test
(This is the most common test to detect cervical cancer. A test that involves collecting cells from the cervix and microscopically evaluating them.
The cervix can contain abnormal cells that could be an early symptom of cervical cancer, which can be found by this test. Women should start getting Pap tests at age 21 and should do so every three years)
HPV test
(The human papillomavirus, which could result in cervical most cancers, may be detected through an HPV check).
Usually, a Pap smear is performed in addition to this test. It might be advised that you have both a Pap smear and an HPV test if you’re over 30)
Factors that trigger cervical cancer:
Weak immunosystem
A weakened immune gadget can be unable to fight the human papillomavirus (HPV), an important reason of cervical cancers, which may increase the risk of getting the disorder.
The virus can be able to modify cervix cells in a way that could cause cancer if the immune device cannot characterize well.
It’s crucial to discuss immune system treatment options with your doctor.
Smoking
Cervical cancer risk can be increased by inhaling someone else’s cigarette smoke. If you share a home with one, ask a smoker to smoke outside or give up smoking entirely. It’s critical to stop smoking as soon as possible if you smoke yourself.
Secondhand smoke is said to be more harmful to health.It can expand different illnesses like lung cancer, asthma, cervical most cancers, and others
History of STD
The possibility of getting cervical cancer can be raised by a history of STIs (sexually transmitted diseases). Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one such STI that would regulate cervix cells and ultimately, result in cancer. Regular cervical cancer screenings, STI prevention strategies, safe sex, condom use, and routine testing are essential.
Less hygiene
Poor hygiene habits increase cervical cancer risk due to reproductive system infections and inflammation.
Regular hand washing is crucial to lowering your risk, especially before and after intercourse. Do not use vaginal liquid soap or other items that can disturb the average balance of germs in the vagina.
To identify any early cancer indications, it’s also crucial to undergo routine cervical cancer tests.
Moisture in the area
Moisture in the vagina and surrounding area increases the risk of cervical cancer by breeding bacteria.
Maintain proper hygiene by keeping the area dry, especially after swimming, and avoiding infection by wearing comfortable, breathable clothing.
Additionally, getting routine screenings for cervical cancer may help find early warning signs of a disease like cervical cancer.
Multiple partners during sex
The more the sex partner more chances of getting infections because of less hygiene and the chances are increased for the growth of HPV.
Prevention from cervical cancer
- Get a vaccination against HPV: Cervical most cancers can be carried via way of the not unusual sexually transmitted contamination known as the human papillomavirus (HPV). The HPV vaccine works in opposition to the HPV traces most in all likelihood that result in maximum cancers.
- Practice safe sex: To lower your chance of getting HPV and other STDs, practice safe sexual activity and use condoms when having sex.
- Maintaining a balanced diet: eating a diet high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help in lowering cancer getting rate.
- Get rid of smoking: Smoking increases the possibility of cervical cancer. Smoking can develop the cancer cells in your body.
- Get a Pap test regularly: A Pap test can find abnormal cervical cells before they develop into cancer. The Pap test should be performed every three years on females between the ages of 21 and 65.
- Practice good hygiene: HPV and other sexually transmitted illnesses can be prevented from spreading by practicing good hygiene. By maintaining a clean genital area and routinely washing your hands.
- Know your family history: Cervical cancer may be more likely to affect women with a family history.
- Restrict your variety of sexual partners: Your probabilities of growing HPV and different STDs boom with the wide variety of sexual companions you've got.
- Get sufficient sleep: To hold your immune system strong and decrease your threat of most cancers and different ailments, it is vital to get sufficient sleep every night time.
- Manage stress: Your immune system may weaken by constant tension, making it harder for your body to fight against infections and diseases like cancer.
Treatments for cervical cancer:
- Surgery: The uterus, cervix, or malignant tissue may all be removed during surgery which is cancerous.
- Radiation therapy: Cancer cells are destroyed by radiation therapy using high-energy X-rays.The usage of radiation remedy is elective; it's also viable to mix it with different treatment options.
- Immunotherapy: Through immunotherapy, cancer is attacked by the body's immune system. The usage of radiation therapy is optional; it is also feasible to mix it with other therapies. Tablets that give a boost to the immune system can be used in some point of immunotherapy.
- Palliative care: Treating advanced most cancers sufferers' signs and symptoms and improving their excellent of life. Sufferers with superior disorders can also receive palliative care further to traditional cancers remedy or as their principal course of remedy.
- Cryotherapy: the removal of abnormal cervical cells using freezing temperatures.
- Practice good hygiene: HPV and other sexually transmitted illnesses can be prevented from spreading by practicing good hygiene. By maintaining a clean genital area and routinely washing your hands.
- Know your family history: Cervical cancer may be more likely to affect women with a family history.
- Restrict your variety of sexual partners: Your probabilities of growing HPV and different STDs boom with the wide variety of sexual companions you've got.
- Get sufficient sleep: To hold your immune system strong and decrease your threat of most cancers and different ailments, it is vital to get sufficient sleep every night time.
- Manage stress: Your immune system may weaken by constant tension, making it harder for your body to fight against infections and diseases like cancer.
Conclusion
A dangerous condition that many women experience worldwide is cervical cancer. Fortunately, there are numerous methods to save you from cervical cancer including having annual Pap exams, getting an HPV vaccine, and following secure sexual practices.
To discover the ailment early, girls ought to speak about the danger of cervical cancer with their doctors and go through ordinary checkups.
